A C Lassification Used to Describe a Stars Unique Spectrum
2 b Sirius has an intensity of 118 10 7 Wm 2 at the Earth. Every element and combination of elements has a unique fingerprint that astronomers can look for in the spectrum of a given object.

Stellar Classification Astronomy Britannica
Remember to check both the Neutral spectra and the Ionic spectra.
. The star emits light over the entire electromagnetic spectrum from the x-ray to the radio. After analysing and comparing the performance of both systems in the. The spectrum of a star is composed primarily of blackbody radiation--radiation that produces a continuous spectrum the continuum.
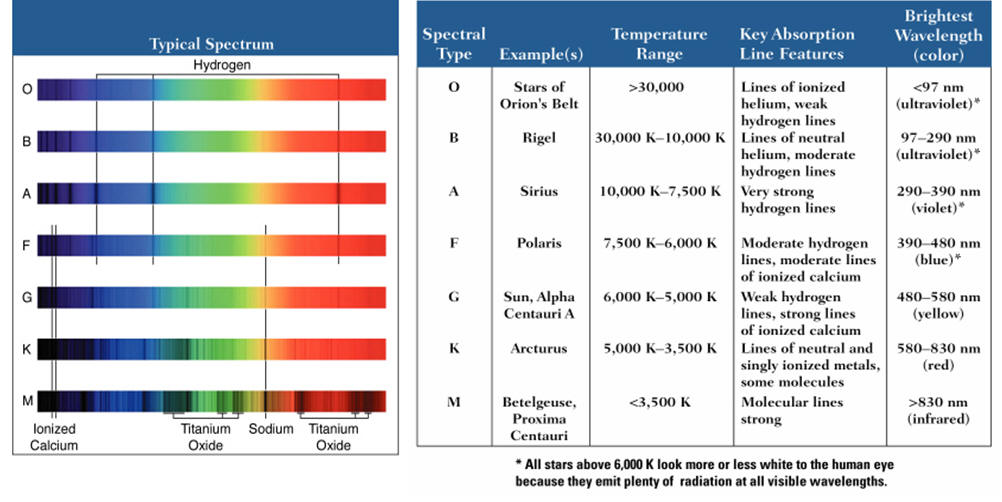
O class stars are blueUV. Firstly the Harvard system of stellar classification is a one-dimensional system in which the stars are classified into 7 main categories according to their spectrum. This spread-out light is called a spectrum.
Because stars are made if a mix of many different elements and all of the different lines for the elements appear in the spectrum. The other three classes are infrared. The Sun is a as a G2V type star a yellow dwarf and a main sequence star.
Stars are classified by their spectra the elements that they absorb and their temperature. How many of the lines of the stars spectra match up with the one from hydrogen. This system is referred to as the Morgan Keenan system.
_____ Drag the. The subtle differences in each type. Relative velocity can be measured by the red or blue shift of the emission or absorption lines.
The Morgan-Keenan MK system is used in modern astronomy a classification system to organize stars according to their spectral type and luminosity class. One of class IV is called a subgiant. The peak emission of their blackbody radiation comes at a.
O and B stars are uncommon but very bright. B class are blue-white A class white F yellow-white G yellow K orange and M red. Up to 24 cash back Classify.
Stars can be classified by their surface temperatures as determined from Wiens Displacement Law but this poses practical difficulties for distant stars. However because of the huge mass of stars these changes are so slow they. Most stellar spectra contain absorption lines that are produced by certain atoms and molecules in the stellar atmospheres such as helium hydrogen heavy elements and molecules.
In summary a stars spectrum presents information about its mass temperature luminosity radius and chemical composition and can also be used in some cases to identify and measure rotational velocity surface expansion or contraction the strength of magnetic fields the presence and speed of stellar winds and the composition of circumstellar. However stars do not emit the same amount of energy at all wavelengths. There are seven main types of stars.
How many of the lines of the stars spectra match up with the. The system was introduced by William Wilson Morgan and Philip C Keenan in 1943. This classification is based on the surface temperature of the star.
The main star in each spectral type is represented by the number 0 and the number increases as the temperature decreases moves toward cooler spectral type. S rapid variations 10 mags in 1 to 10 days A blue to white star B yellow to red star T T Tauri variables intense iron emission lines YY spectral evidence for infalling matter. The Roman Numerals indicate the stars luminosity and start with.
As the chemical composition changes the spectrum changes. Spectrum next to the. We propose and discuss the application of artificial intelligence techniques to the classification of stellar spectra.
Then use the table above to classify each star and describe its surface temperature. The Sun a dwarf star of type G2 is classified as G2 V. A star of luminosity class II falls between giants and supergiants.
Use the Gizmo to find the elements that are present in the spectra of stars 1 through 4. There are several subspecies indicated by one or more suffixes. The spectrum indicates the chemical composition of each star.
Apart from these three the spectrum can be used to help determine. So that the edges line up. L class appear very deep red in visual light.
Density Mass Distance Luminosity One interesting factor is how much the emission lines or absorption lines are spread. Ionized carbon oxygen and silicon are seen. Their spectra show methane.
This is done through the use of the numbers 0 - 9 and the Roman Numerals I - VII. Spectrum next to the. Two types of systems are considered knowledge-based systems Expert Systems and different classes of neural networks.
The classification of Stars Atlas of the Universe. These are the light. The letter N is omitted if there is no association with a nebula.
Star Apparent magnitude Absolute magnitude Spectral class Sirius 14 14 A Rigel 012 71 B a State the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The stellar spectra when examined in greater detail contain a wealth of information that can be used to describe various physical properties of the star see figure. To see its absorption spectrum.
The distance between Sirius and the Earth is 813 10 13 km. Star Color Elements in spectrum Class Surface Temperature K 1 2 3 4 2. T class are cooler than L class.
The star Pi Cephei classified as G2 III is a giant falling between G0 and K0 but much closer to G0. M stars are. The Ib suffix means that it is a moderately luminous supergiant.
In order of decreasing temperature O B A F G K and M. Their spectra show alkali metals and metal hydrides. A 7500 to 10000 K blue white A stars have the strongest hydrogen lines recall the ordering of the original Harvard.
The following is the spectrum of the sun. This might indicate a surrounding protoplanetary disc or suchlike. The 7 categories are denoted by 7 alphabets which from hotter to colder are O B A F G K M.
Spectral characteristics offer a way to classify stars which gives information about temperature in a different way - particular absorption lines can be observed only for a certain range of temperatures because only in that range are. Each element have an a electromagnetic spectrum of emision and absorption each code for each element has been experimentally determined by zooming the light of a star and throwing it through a prisma the light will be suitable to determinate his electromagnetic spectrum. B 10000 to 30000 K blue white In stars in this spectral class the hydrogen lines are stronger than in O stars while the lines of ionized helium are weaker.
Unique to the star and to the stage the star occupies in its lifestyle Why is it often difficult to identify a stars elements from its absorption spectrum.
Classification Of Stellar Spectra

The Spectra Of Stars And Brown Dwarfs Astronomy

Remote Sensing Vector Illustration Satellite Data Wave Acquisition Scheme Educational Active And Passive Inf Remote Sensing Remote Sensing And Gis Satellites

Classifications Of Air Conditioning Systems Http Techshoreinspections Blogspot Com 2016 12 Techshore Inspection Air Conditioning System Ac System Conditioner
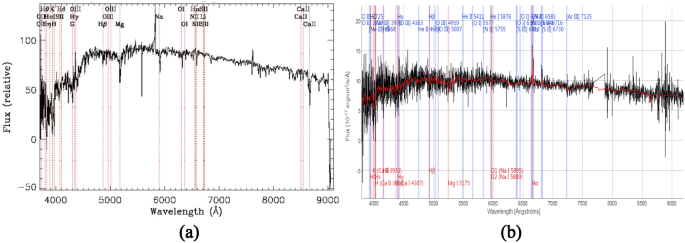
Spectral Classification And Particular Spectra Identification Based On Data Mining Springerlink
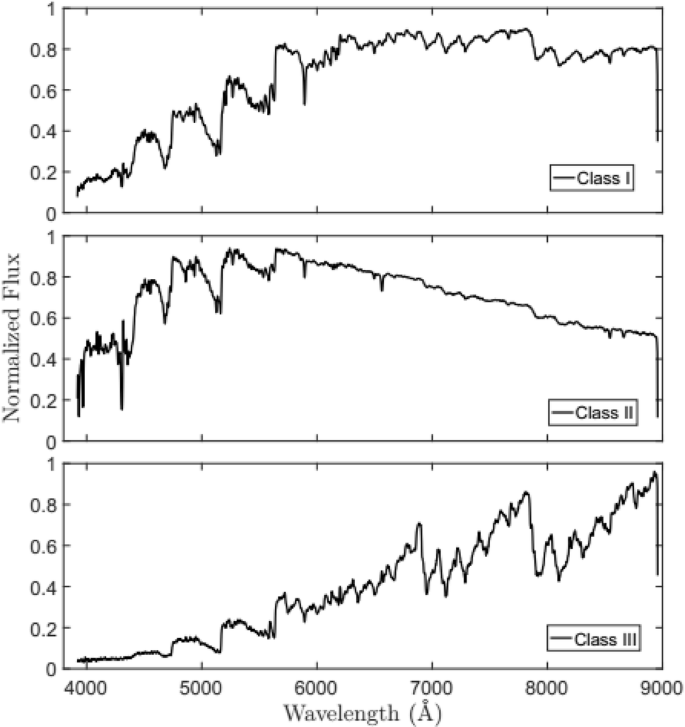
Spectral Classification And Particular Spectra Identification Based On Data Mining Springerlink
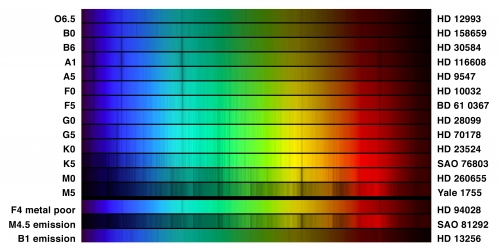
Colors Temperatures And Spectral Types Of Stars Astronomy 801 Planets Stars Galaxies And The Universe

Stellar Classification Javalab
Classification Of Stellar Spectra

The Spectra Of Stars And Brown Dwarfs Astronomy

Stellar Classification Astronomy Britannica

Pin By Beth Froman Brown On Science Physics Physics Classroom Weather Science
Classification Of Stellar Spectra
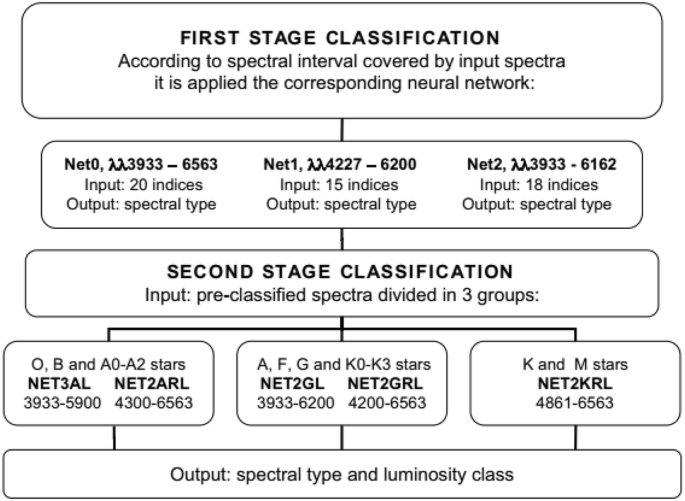
Spectral Classification And Particular Spectra Identification Based On Data Mining Springerlink
Analysis Of Spectra In Astrophysics Visiting The Old Learning Of The New Universe Of Spectroscopy

Comments
Post a Comment